State of New York
New York is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the Northeastern United States. New York was one of the original thirteen colonies that formed the United States. With more than 19 million residents in 2019,[6] it is the fourth-most-populous state. To distinguish it from New York City, which is the largest city in the state, it is sometimes referred to as New York State.
Two-thirds of the state’s population lives in the New York metropolitan area (including nearly forty percent on Long Island).[9] The state and city were named for the 17th-century Duke of York, the future King James II of England. With an estimated population of 8.34 million in 2019,[9] New York City is the most populous city in the United States and the premier gateway for immigration to the United States.[10][11][12] The New York metropolitan area is one of the most populous in the world.[13][14] A global city,[15] NYC is home to the United Nations Headquarters,[16] and has been described as the cultural,[17][18] financial,[19][20] and media capital of the world,[21][22] as well as the world’s most economically powerful city.[23][19][24] The next four most populous cities in the state are Buffalo, Rochester, Yonkers, and Syracuse, while the state capital is Albany.
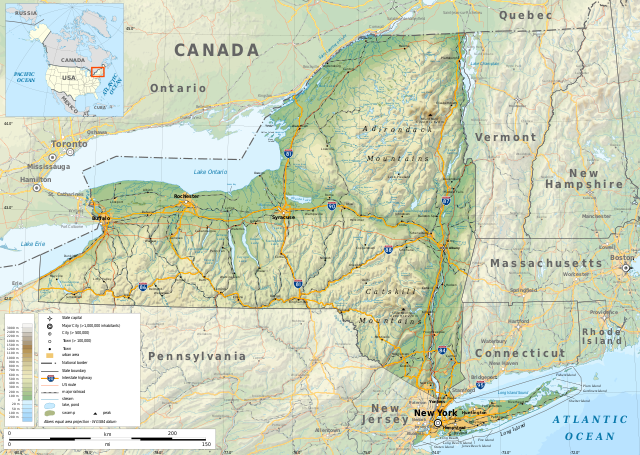
The 27th largest U.S. state in land area, New York has a diverse geography. The state is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south and Connecticut, Massachusetts, and Vermont to the east. The state has a maritime border with Rhode Island, east of Long Island, as well as an international border with the Canadian provinces of Quebec to the north and Ontario to the northwest. The southern part of the state is in the Atlantic coastal plain and includes Long Island and several smaller associated islands, as well as New York City and the lower Hudson River Valley. The large Upstate New York region comprises several ranges of the wider Appalachian Mountains, and the Adirondack Mountains in the northeastern lobe of the state. The north–south Hudson River Valley and the east–west Mohawk River Valley bisect these more mountainous regions. Western New York is considered part of the Great Lakes region and borders on Lake Ontario, Lake Erie, and Niagara Falls. The central part of the state is dominated by the Finger Lakes, a popular vacation and tourist destination.
New York had been inhabited by tribes of Algonquian and Iroquoian-speaking Native Americans for several hundred years by the time the earliest Europeans came to New York. French colonists and Jesuit missionaries arrived southward from Montreal for trade and proselytizing. In 1609, the region was visited by Henry Hudson sailing for the Dutch East India Company. The Dutch built Fort Nassau in 1614 at the confluence of the Hudson and Mohawk rivers, where the present-day capital of Albany later developed. The Dutch soon also settled New Amsterdam and parts of the Hudson Valley, establishing the multicultural colony of New Netherland, a center of trade and immigration. England seized the colony from the Dutch in 1664. During the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), a group of colonists of the Province of New York attempted to take control of the British colony and eventually succeeded in establishing independence. In the 19th century, New York’s development of the interior, beginning with the Erie Canal, gave it incomparable advantages over other regions of the east coast and built its political and cultural ascendancy.[25]
Many landmarks in New York are well known, including four of the world’s ten most-visited tourist attractions in 2013: Times Square, Central Park, Niagara Falls, and Grand Central Terminal.[26] New York is home to the Statue of Liberty.[27] In the 21st century, New York has emerged as a global node of creativity and entrepreneurship,[28] social tolerance,[29] and environmental sustainability.[30][31] New York has approximately 200 colleges and universities, including the State University of New York. Several have been ranked among the top 100 in the nation and world.[32][33][34]